9.3 Overriding Superclass Methods
In a class hierarchy, when a method in a subclass has the same name and type signature as a method in its superclass, then the method in the subclass is said to override the method in the superclass. When an overridden method is called from within a subclass, it will always refer to the version of that method defined by the subclass. The version of the method defined by the superclass will be hidden.
A subclass may call an overridden superclass method by prefixing its name with the super key word and a dot (.). Consider the following:
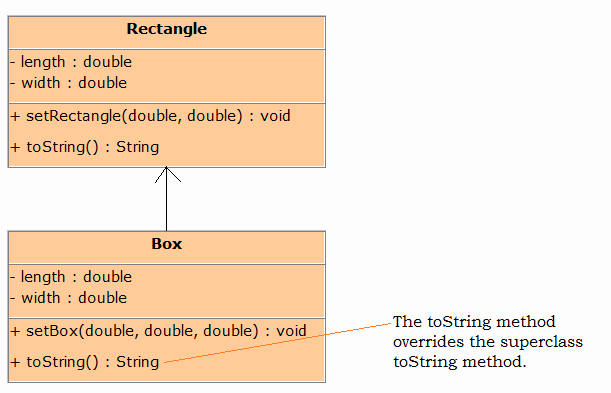
Program (Rectangle.java)
public class Rectangle
{
private double length;
private double width;
/**
* Sets length and width of rectangle.
*/
public void setRectangle(double length, double width)
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
/**
* Returns length and width as string
*/
public String toString()
{
return "Length : " + length + "\nWidth : " + width;
}
}Program (Box.java)
public class Box extends Rectangle
{
private double height;
/**
* Sets length, width and height of box.
*/
public void setBox(double length, double width, double height)
{
setRectangle(length, width);
this.height = height;
}
/**
* The toString method overrides the Rectangle's toString method
* and returns length, width and height of box as string
*/
public String toString()
{
return super.toString() + //Calling Rectangle's toString method
"\nHeight : " + height;
}
}Program (BoxDemo.java)
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* This program demonstrates the Box class.
*/
public class BoxDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double length, width, height;
// Create a Scanner object for keybaord input.
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
// Get the length of box.
System.out.print("Enter the length of box : ");
length = console.nextDouble();
// Get the width of box.
System.out.print("Enter the width of box : ");
width = console.nextDouble();
// Get the height of box.
System.out.print("Enter the height of box : ");
height = console.nextDouble();
// Create a box object.
Box myBox = new Box();
// Set the length, width and height of box.
myBox.setBox(length, width, height);
// Display the box detalis.
System.out.println(myBox);
}
}Output :
Enter the length of box : 34.5
Enter the width of box : 5.6
Enter the height of box : 3.2
Length : 34.5
Width : 5.6
Height : 3.2